What is “Sickle Cell”?
Sickle Cell is a genetic blood disorder that is passed from the parent to the child. Genes are what determine a child’s physical traits such as skin, eye and hair color. Genes also affect hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein in the red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. People with normal hemoglobin received two normal genes denoted as AA.
Abnormal genes are common and can also be transferred to children. Both parents contribute one gene for each trait. When a person has Sickle Cell Trait (SCT) the gene type is AS, which is one normal gene and one abnormal gene. A person who has Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) has a gene type of SS.
If one parent has SCT (AS) and the other parent has normal hemoglobin (AA) there is a 50% or 1 in 2 chance that each of their children will have the Sickle Cell gene, creating SCT (AS). If both parents have AS, there is a 25% or 1 in 4 chance that each of their children will have two Sickle Cell genes, creating SCD (SS). For a visual understanding of the family risk associated with Sickle Cell Disease and Trait, please CLICK HERE.
The abnormal hemoglobin causes the red blood cells to sickle and lose their oxygen. When red blood cells sickle they become hard, sticky, and crescent shaped. These cells create blockages in blood vessels. These blockages make it difficult for normal red blood cells to pass through the blood vessels with vital oxygen and nutrients the body needs.
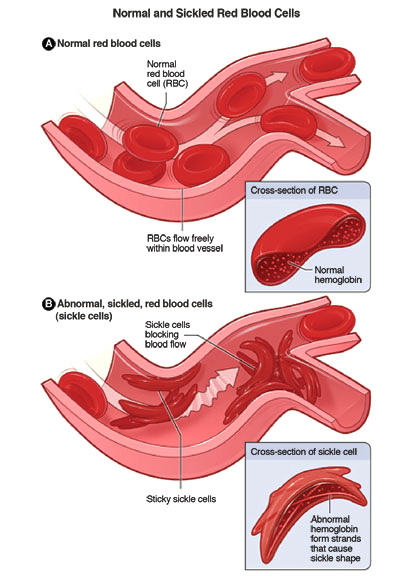
If a person has SCD, they are prone to more serious health conditions.
Examples of health complications include the following:
- Leg Ulcers
- Acute Chest Syndrome
- Jaundice
- Pneumonia
- Pain Episodes
- Organ Damage
- Slowed Growth and Delayed Puberty in Children
- Heart Problems
- Joint Damage
- Increased Risk of Infections
- Stroke
- Anemia
While the disease is often debilitating and even deadly, successful treatments are increasing life expectancy with the advancement of medical science.
The following are just a few available medical treatments:
- Hydroxyurea
is an oral medication that is used to increase fetal hemoglobin (HbF) in the body. When Hbf is increased, it also raises the total hemoglobin in the body. Fetal hemoglobin is used to promote healthy blood cells in the body and reduce the risk of cells sickling. - Blood Transfusions
A blood transfusion provides new blood with red blood cells and oxygen to the body. When this happens, it can reduce the amount of blockage that can occur with sickled cells, allowing oxygen rich blood to pass through unrestricted. - Bone Marrow Transplant
This therapy replaces a person’s bone marrow. The bone marrow is where the production of red blood cells occurs.
For more information on any of our programs please contact the Center today at 317-927-5158 or email information@themartincenter.org
